Do you find yourself creating new models in the COMSOL Multiphysics® software faster than you can launch them interactively in the COMSOL Desktop® environment? If having to wait for your current model to finish solving before launching the next one does not sound appealing, it’s time to learn how to run your simulations in Batch mode from the command line. As it turns out, this is quite a simple process.
Why Run COMSOL Multiphysics® in Batch Mode from the Command Line?
If you have used simulation tools for any significant period of time, you may have found yourself creating new models faster than your computer can solve them. This is especially common if your models are quick to set up but take a fair amount of time to solve. Running multiple models at the same time on the same computer is not a good option, as they would compete for resources (RAM, in particular) and therefore take longer to run simultaneously than they would sequentially, or back to back.

So, what’s a modeler to do?
You could launch your first model in the graphical user interface (GUI) and wait for it to solve, launch the second model in the GUI and wait for it to solve, and so on. But who would want to return to the office after hours or on weekends just to launch their next model?
Fortunately, there is a solution: creating a shell script, or a batch file, which automatically launches your COMSOL Multiphysics simulations one after the other. I’ll explain how to do this step by step on a computer with the Windows® operating system, but these ideas also apply to the other supported platforms (macOS and the Linux® operating system).
How to Run a Single Model from the Command Line
Let’s start with a demonstration of how to run a single COMSOL Multiphysics model from the command line.
First, we create a model file in the COMSOL Multiphysics GUI, also known as the COMSOL Desktop. Since we’re going over how to use a new functionality, the smaller and less detailed the model, the better. This will allow us to understand the functionality and perform tests on it quickly. Once you are comfortable with this functionality, it can, of course, also be applied to sophisticated models that take a long time to solve.
At this stage, we check that the model is properly set up by running it with a relatively coarse mesh. This presents the additional benefit of generating a default data set and one or two default plots in the Study branch of the model tree. Now that we’ve ensured that the model is properly set up, we can refine the mesh and save the file under the name Model1.mph in our working folder. In this example, that’s C:/Users/jf.
At this point, we can close the COMSOL Desktop.
Next, we open a Command Prompt window and, at the command line, make our way to our working folder. We type the name of the working folder:
cd C:\Users\jf
Then, we press the Enter key.
We are just about to call the COMSOL® software using the comsolbatch command. Before we can do that, we need to make sure that the Windows® operating system knows where to find that command. This is where, if we have not done so before, we add the path to the COMSOL® software executables to the Windows® path environment variable. On a computer running Windows®, with a default installation, these executables are located in C:\Program Files\COMSOL\COMSOL52a\Multiphysics\bin\win64.
Now, drum roll, please!
Back at the command line, we type the following command and then press Enter:
comsolbatch -inputfile Model1.mph -outputfile Model1_solved.mph
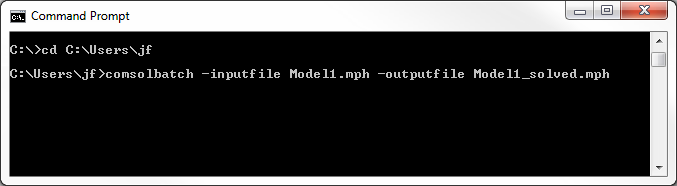
This command instructs Windows® to launch COMSOL Multiphysics® in Batch mode, hence without a graphical user interface. As the syntax suggests, we use Model1.mph as an input and the file Model1_solved.mph is the file with the solution. If we were to omit the “-outputfile Model1_solved.mph” part in the command above, the solution would be stored in the input file, Model1.mph.
As the software runs, some progress information is displayed at the command line. After a few moments, the run is done and we can open the output file, Model1_solved.mph, in the GUI. We can see that the model has indeed been solved and that we can postprocess the results interactively, just as if we had computed the solution in the COMSOL Desktop.
Writing and Running a Shell Script
Now that we’ve figured out how to launch a COMSOL Multiphysics model from the command line, let’s see how to automate running two or more simulations in a row.
Let’s create a second model, check that it is properly set up, and save the file to our working folder under the name Model2.mph. With that done, we can close the COMSOL Desktop again.
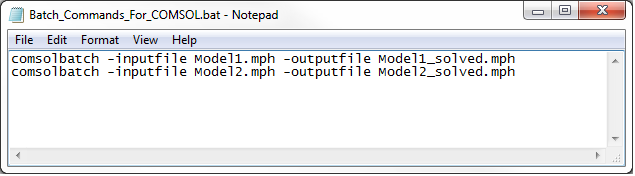
Using a text editor like Notepad, we create a plain text file containing the following two lines:
comsolbatch -inputfile Model1.mph -outputfile Model1_solved.mph
comsolbatch -inputfile Model2.mph -outputfile Model2_solved.mph
We then save this in our working folder as a plain text file with the .bat extension. Here, we named the file Batch_Commands_For_COMSOL.bat.
At the command prompt, still in our working folder, we launch Batch_Commands_For_COMSOL.bat. At the command line, we type:
Batch_Commands_For_COMSOL
Then, we press the Enter key.
COMSOL Multiphysics will run without the GUI open and solve the problem defined in the file Model1.mph. The COMSOL® software will then do the same for the problem defined in the file Model2.mph. Once the runs are finished, we can inspect the files Model1_solved.mph and Model2_solved.mph in the COMSOL Desktop to see that they indeed contain the solutions of these two analyses. On the other hand, if we open the files Model1.mph and Model2.mph in the GUI, we see that they have not changed and still contain the problem definitions, but no solutions.
If we want to run more than two files sequentially, we can just modify the .bat file accordingly and add lines for each file that we wish to run.
By learning how to run your COMSOL Multiphysics simulations in Batch mode from the command line, you will be able to complete your projects more efficiently and with ease.
Further Resources
- Learn more about the modeling capabilities of COMSOL Multiphysics in these core functionality blog posts
- Watch this introductory tutorial video on how to set up and run a simulation
Microsoft and Windows are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
macOS is a trademark of Apple Inc., in the U.S. and other countries.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the U.S. and other countries.



Comments (20)
Min Yao
December 20, 2016Helpful content! Also wondering how to pick which study to calculate in the model. It will automatically run every study in the specified model right? Thanks~
Jeff Hiller
December 20, 2016Hi Min,
I am glad you found it helpful.
Yes, you can specify which study to compute in the model, using the -study option followed by the study tag. See the COMSOL Multiphysics Reference Manual, page 1299.
Jeff
Niklas Rom
December 23, 2016Hi Min, there are more handy things you can do. For example, to sweep a parameter p1 over a number of values, use the switches
-pname p1 -plist 1,2,3,4,5
Josh Thomas
December 29, 2016Jeff-
Thanks for the helpful article. Works great for Windows! Would you be able to post the Linux step-by-step instructions, too? I am particularly interested in how to run the shell script on Linux.
-Josh
Jeff Hiller
January 3, 2017Hi Josh,
I have not used Linux in some time (Understatement of the year), so I wouldn’t venture to write step-by-step instructions on how to run a shell script on Linux. This link looks pretty good as an introduction to the topic: http://linuxcommand.org/writing_shell_scripts.php .
As for the COMSOL command to use, on Linux and Mac it is
comsol batch -inputfile Model1.mph -outputfile Model1_solved.mph
and you will find detailed information on COMSOL commands for Linux in the COMSOL Multiphysics Reference Manual, version 5.2a, starting on page 1301. For Macintosh, the corresponding section starts on page 1313.
Jeff
David Reens
January 30, 2017Is there any way to set up a model in such a way that derived values are also evaluated by a comsolbatch call from the command line? I have some memory intensive surface integration derived values that I’d like to run on a machine I have access to with no GUI and tons of RAM. Or maybe when comsolbatch is performed on a model it does all of the derived values too by default?
Thanks,
Dave
Jeff Hiller
January 31, 2017Hi David,
The comsolbatch call runs the solver sequence. However, you may be able to reframe your derived value as a Probe and force its evaluation through the solver sequence.
As you prepare your files, the approach is then very similar to the one presented in this other blog https://www.comsol.com/blogs/the-power-of-the-batch-sweep/ , except that you would not be sweeping a parameter, and therefore you would use a Batch node instead of a Batch Sweep node.
Other than that, you’d similarly set up the probe, make sure that it’s evaluated in the study step of interest, and before running the file possibly set up your probe table so it is saved to a plain text file (This way you don’t need to open the mph file to see the value of the probe). And of course, you’d run all the model files you prepared that way via a script as described above.
You’ll want to try this out with a few small models first, and then move on to your large models. Please contact our Technical Support team should the rough outline above not be sufficient/clear.
Jeff
Victor Zermeno
May 12, 2017Hi Jeff,
Very interesting post. Thanks for sharing.
Is there a way to clear all solutions in a Comsol file from the command line without running the model? Something like:
comsolbatch -inputfile myfile.mph -norun -clearall -outputfile myfile.mph
Cheers,
Victor
Jeff Hiller
May 12, 2017Hello Victor,
No, not to my knowledge.
Best,
Jeff
Ying Tang
May 17, 2017Hi Jeff,
I have a question regarding to export the table.
I am doing a parameter sweep in command line. after each batch I want to have my table saved to a txt file automatically. However everytime I finish a new batch, the export table file will just overwrite the old table file since the filename define in COMSOL GUI is the same. Changing the export table filename in the COMSOL GUI is not practical since there are so many batch runs.
How can I automatically export the table and save it with different names?
Thank you for the answer in advance.
Ying
Jeff Hiller
May 17, 2017Hello Ying,
Since this is only tangentially related to the topic of the blog post, I’ll invite you to please contact COMSOL Support (www.comsol.com/support) for assistance with your question.
Best regards,
Jeff
Nikolaj Feidenhans'l
June 19, 2017Instead of adding a folder to the Windows® path environment variable, you can instead add the executable folder to the shell script. Like this:
SET EXE_PATH=C:\Program Files\COMSOL\COMSOL53\Multiphysics\bin\win64
“%EXE_PATH%\comsolbatch” -inputfile Model1.mph
“%EXE_PATH%\comsolbatch” -inputfile Model2.mph
Jeff Hiller
July 13, 2017David Reens,
Another approach to your query is provided by this recent blog:
https://www.comsol.com/blogs/how-to-use-job-sequences-to-save-data-after-solving-your-model/
Best,
Jeff
Yi Yan
April 2, 2019Hi Jeff,
Thank you for your post, this is extremely useful.
I am just wondering if you have any idea about how to add the path of COMSOL bash command to a Linux cluster. COMSOL has been successfully installed in that system.
Thank you very much,
Yi
Jeff Hiller
April 3, 2019Hi Yi,
Sorry, no I don’t.
Jeff
Kriti Agarwal
February 19, 2020Within the same batch file is there any way to run two comsol files in parallel?
Jeff Hiller
February 19, 2020 COMSOL EmployeeHi Kriti,
I believe the commands in a .bat file are always run sequentially. I could be wrong about that. But in any case you have to bear in mind that if you run two models at the same time they will compete for resources. If the models are small relative to the computer, that’s fine, but if not, it is quite possible that it would take more time for the models to run simultaneously than sequentially.
Jeff
Shant
April 14, 2021Hi Kriti,
Why do not use a batch sweep in that case?
Here is the illustration:
https://www.comsol.com/blogs/the-power-of-the-batch-sweep/
mehran jooya
February 27, 2020Hi Mr.Hiller
I’m using comsol multiphysics on a cluster (or server) that operate linux os(cent os). i used this command to run and solve my mph file that named s4: ‘comsol batch -inputfile s4.mph -outputfile s4solve.mph’ then i downloaded s4solve.mph and opened it with my system. but the output file does not have results. while the size of file rised from 1mb to 1.55 Gb.
thanks
Sanjay Kumar
December 11, 2023what if the .mph has a password to open ?