Permanent Magnet Motor in 3D
Application ID: 47621
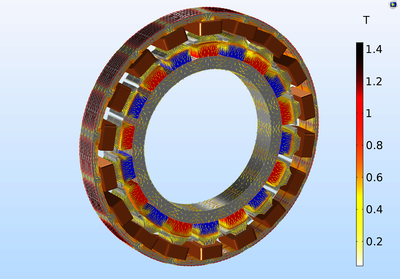
Permanent magnet (PM) motors are used in many high-end applications, such as in electric and hybrid vehicles. An important design limitation is that the magnets are sensitive to high temperatures, which can occur through heat losses caused by currents, particularly eddy currents.
In this tutorial, an 18-pole PM motor is modeled in 3D to accurately capture eddy current losses in the magnets. The central part of the geometry, containing the rotor and part of the air gap, is modeled as rotating relative to the coordinate system of the stator. Sector symmetry and axial mirror symmetry are leveraged to reduce the computational effort while still capturing the full 3D behavior of the device.
This model example illustrates applications of this type that would nominally be built using the following products:
however, additional products may be required to completely define and model it. Furthermore, this example may also be defined and modeled using components from the following product combinations:
The combination of COMSOL® products required to model your application depends on several factors and may include boundary conditions, material properties, physics interfaces, and part libraries. Particular functionality may be common to several products. To determine the right combination of products for your modeling needs, review the Specification Chart and make use of a free evaluation license. The COMSOL Sales and Support teams are available for answering any questions you may have regarding this.
